출처
접근
Backtracking
특정 단어를 한 글자씩 찾아들어가면서 단어 사전에 존재하는지 확인하는 방식은 전형적인 DFS의 형태입니다.
- 주어진 단어의 개수가
w < 300,000이지만 탐색해야 하는 전체Boggle보드의 크기가4X4이고, 이러한Boggle의 개수가b < 30이기 때문에 DFS 자체는 많은 시간복잡도가 필요하지 않습니다. DFS탐색 과정에서 다음 글자를 추가했을 때, 단어 사전에 포함된 단어를 만들 수 있는지를 빠르게 확인하여 불가능한 경우를 가지치기(pruning)한다면, 시간복잡도를 더욱 줄일 수 있습니다.
이러한 기법을 Backtracking이라고 합니다.
Trie
단어 사전에 현재 단어가 포함되어 있는지를 확인하는 기법에는 여러 가지가 있지만, 저는 Trie1 자료구조를 통해 단어를 저장하고, 이렇게 저장된 노드를 활용해서 다음 노드로 탐색할지 여부를 결정하였습니다.
문제에서 주어진 예시를 Trie 형태로 저장하면 다음과 같습니다.
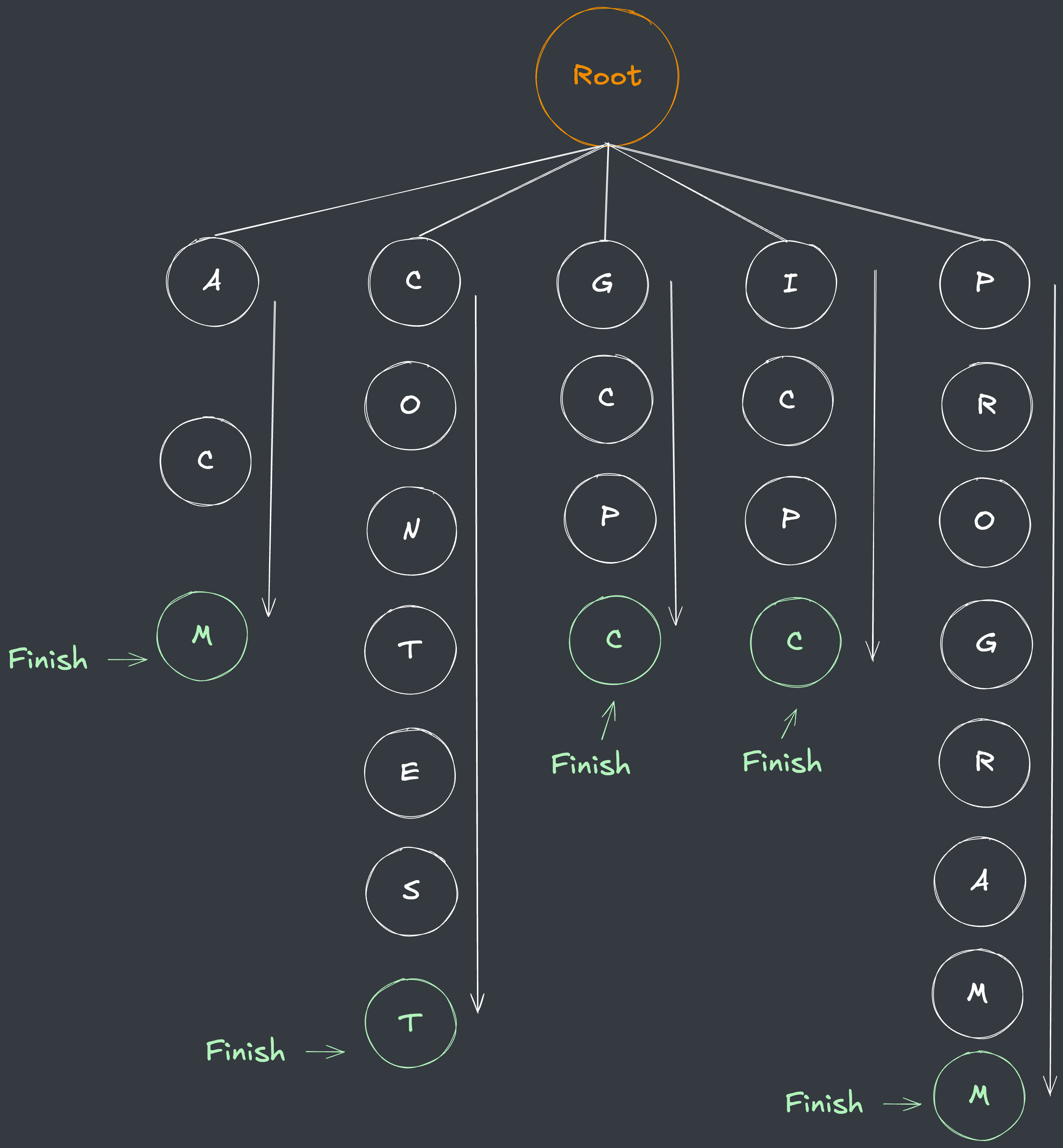
- Root 노드로부터 각 알파벳을 하나씩 갖는 자식 노드들을 순차적으로 저장합니다.
- 마지막 노드 위치에 단어가 있다는 것을 표시하기 위해
isFinished라는 플래그 값을 별도로 저장합니다.
A -> C -> M순서로 탐색하는 중, 현재 노드인M노드에isFinished값이 있으므로ACM이라는 단어가 사전에 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 만약,
A노드에서C가 아닌 다른 자식을 찾으려고 하면, 단어 사전에 존재하지 않는다는 것을O(1)의 시간복잡도로 확인하는 것이 가능합니다.
풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// 루트 노드 별도로 저장
static Node root;
// Trie 노드
static class Node {
char c;
Node[] children;
boolean isFinished;
// 생성자
Node(char c) {
this.c = c;
this.children = new Node[26];
this.isFinished = false;
}
// 자식이 없다면 추가 후 자식 참조값 리턴
Node add(char c) {
Node temp = this.children[c - 'A'];
if (temp != null) return temp;
Node child = new Node(c);
this.children[c - 'A'] = child;
return child;
}
// 자식이 있는지 여부 확인
boolean hasChild() {
if (children == null) return false;
for (Node child : children)
if (child != null) return true;
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
// 루트노드 생성
root = new Node('r');
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
char[] word = br.readLine().toCharArray();
Node temp = root;
// 단어 순서대로 따라가면서 자식 노드 추가
for (char c : word) {
temp = temp.add(c);
}
// 마지막 알파벳에 플래그 표시
temp.isFinished = true;
}
br.readLine();
int b = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
// DFS 결과 저장할 HashSet
Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
// 새로운 boggle 입력
char[][] boggle = new char[4][4];
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
boggle[j] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
}
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
// 첫번째 자식부터 탐색
Node temp = root.children[boggle[r][c] - 'A'];
if (temp == null) continue;
// 첫번째 자식 현재위치에 넣고 탐색 시작
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(boggle[r][c]);
dfs(boggle, result, r, c, temp, sb, new boolean[4][4]);
}
}
printAnswer(result);
result.clear();
if (i != b - 1) br.readLine();
}
}
// DFS + Backtracking
static int[] dr = {0, 0, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1};
static int[] dc = {1, -1, 0, 0, 1, -1, -1, 1};
static void dfs(char[][] boggle, Set<String> result, int r, int c, Node temp, StringBuilder sb, boolean[][] isVisited) {
isVisited[r][c] = true;
// 단어가 있는 위치에 도달하면 해당 단어 추가
if (temp.isFinished) {
result.add(sb.toString());
// 현재 위치 아래에 자식이 없다면 가지치기
if (!temp.hasChild()) return;
}
// 8방향 탐색
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int nr = r + dr[i];
int nc = c + dc[i];
if (nr < 0 || nr >= 4 || nc < 0 || nc >= 4 || isVisited[nr][nc]) continue;
if (temp.children[boggle[nr][nc] - 'A'] == null) continue;
// 다음 단어 추가
sb.append(boggle[nr][nc]);
dfs(boggle, result, nr, nc, temp.children[boggle[nr][nc] - 'A'], sb, isVisited);
// DFS 복귀 후 값 초기화
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
isVisited[nr][nc] = false;
}
}
// 정답 출력
static int[] scoreMap = {0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 11};
static void printAnswer(Set<String> result) {
int maxLength = 0;
int score = 0;
List<String> maxs = new ArrayList<>();
for (String r : result) {
// 총점에 현재단어 길이 점수 추가
score += scoreMap[r.length()];
if (r.length() > maxLength) {
maxLength = r.length();
maxs.clear();
maxs.add(r);
// 가장 긴 단어 여러개일 경우 저장
} else if (r.length() == maxLength) {
maxs.add(r);
}
}
// 가장 긴 단어 여러개일 경우 오름차순 정렬
maxs.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
// 총점 + 가장 긴 단어 + 결과 크기 출력
System.out.println(score + " " + maxs.get(0) + " " + result.size());
}
}
결과
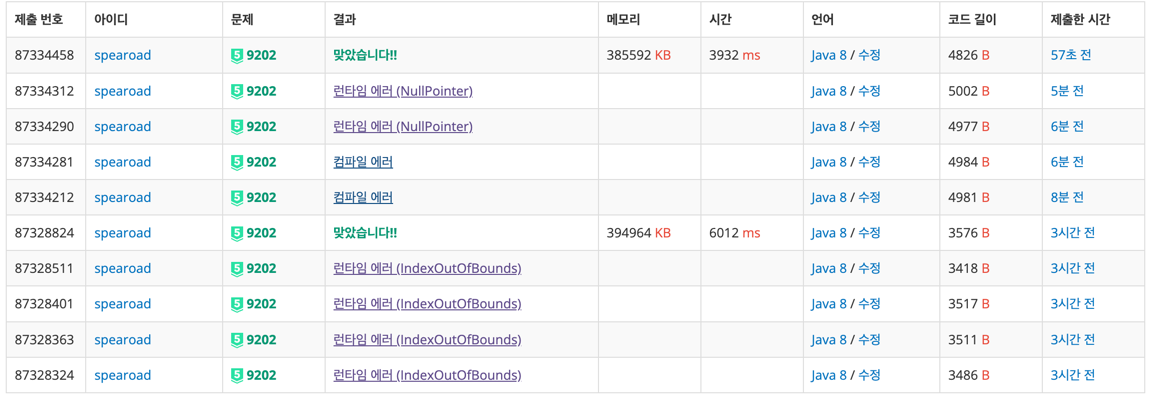
- 소요시간 : 1:55:30
리뷰
자식 노드를 탐색하는 과정에서 발생한 런타임 오류(IndexOutOfBounds)를 해결하는데 너무 오래 걸렸습니다.
DFS를 재귀 형식으로 구현하는게 구현 속도는 빠르지만 디버딩 툴 없이 디버깅하기가 까다로워서 잘 고민해봐야겠습니다.
또한 문제를 풀고 보니 시간 제한이 10초로, 다른 분들의 풀이를 보니 Trie를 활용하지 않고도 Backtracking만 잘 구현한다면 시간복잡도 내로 충분히 풀 수 있는 것 같습니다.
효율적인 알고리즘으로 푸는 것보다, 주어진 시간복잡도 내에서 가장 빨리 구현할 수 있는 알고리즘을 찾는게 중요함을 항상 주의해야겠습니다.
References
| URL | 게시일자 | 방문일자 | 작성자 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backtracking | 2022.02.08. | 2024.12.10. | Wikipedia |